
The possible letters are A, C, G, and T, representing the four nucleotide bases of a DNA strand – adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine – covalently linked to a phosphodiester backbone.

The nucleobases are important in base pairing of strands to form higher-level secondary and tertiary structure such as the famed double helix. Each nucleotide consists of three subunits: a phosphate group and a sugar ( ribose in the case of RNA, deoxyribose in DNA) make up the backbone of the nucleic acid strand, and attached to the sugar is one of a set of nucleobases. Nucleic acids consist of a chain of linked units called nucleotides. Conversely, there is no parallel concept of secondary or tertiary sequence. Primary structure is sometimes mistakenly referred to as primary sequence. Nucleic acids also have a secondary structure and tertiary structure.
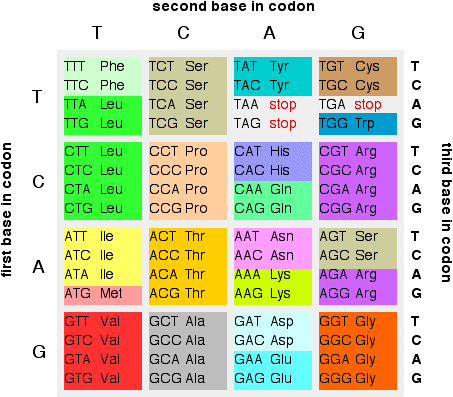
Biological deoxyribonucleic acid represents the information which directs the functions of an organism. The sequence has capacity to represent information. For this reason, the nucleic acid sequence is also termed the primary structure. Because nucleic acids are normally linear (unbranched) polymers, specifying the sequence is equivalent to defining the covalent structure of the entire molecule. By convention, sequences are usually presented from the 5' end to the 3' end.
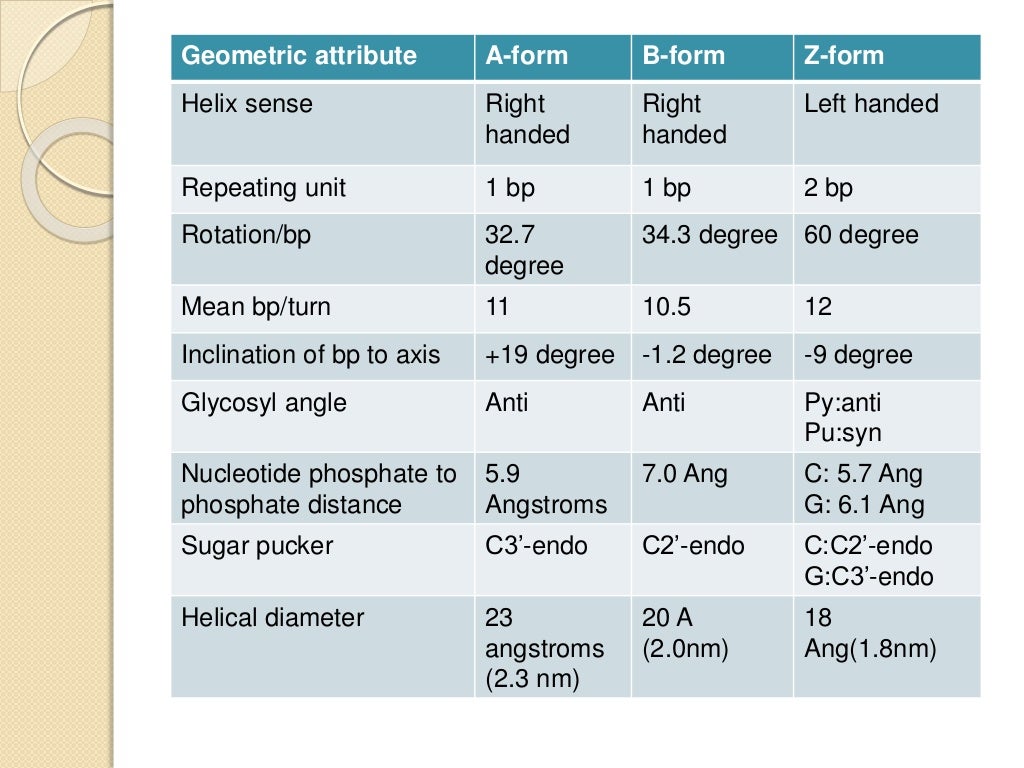
DNA SEQUENCE CHART SERIES
( PDB: ADNA, 1BNA, 4OCB, 4R4V, 1YMO, 1EQZ)Ī nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases signified by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. Interactive image of nucleic acid structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) using DNA helices and examples from the VS ribozyme and telomerase and nucleosome.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
